Guide
Jun 03, 2022
Quickly Build a User Switcher, Just Like Gmail
Anshuman Bhardwaj
Build an app with complete authentication and a user switcher just like gmail has.
Developing an authentication system from scratch can be time-consuming, and the process can be prone to bugs. If you're looking for a customer identity platform that provides user management features like authentication, authorization, and management of user profiles, roles, and permissions, check out Clerk
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to easily implement your own user profile switcher using Clerk and Next.js
What Is Clerk
Clerk is a one-stop solution for authentication and customer identity management. It helps you build a flawless user authentication flow that supports logging in with a password, multifactor authentication, or social logins with providers like Google, LinkedIn, Facebook, and GitHub. Clerk provides components like <SignUp/> and <SignIn/> that you can plug into your application right away to quickly build an authentication flow.
It's common for users to have multiple accounts for different purposes. For instance, you may have a personal YouTube channel for your friends and family, and another one specifically intended for your audience in your work as a developer. With Clerk’s multisession feature, you can seamlessly and intuitively switch between both accounts as needed.
Building a User Switcher
Before you begin building a user switcher, you'll need a code editor like Visual Studio Code
Create your Clerk account
Set Up the Project
To set up the project, run npx create-next-app clerk-app in your terminal. This will initialize a Next.js project. Then you need to run npm install @clerk/nextjs inside the project and open your Clerk dashboard
Save the keys copied above in a .env.local file inside your project:
.env.localNEXT_PUBLIC_CLERK_FRONTEND_API=<frontend-key>CLERK_API_KEY=<backend-api-key>CLERK_JWT_KEY=<jwt-verification-key>
Set Up the Authentication Flow
The authentication flow of your application dictates how the users access different parts of your application. In this example, the user authentication flow works like this:
To begin, implement the authentication flow in the `pages/_app.js`:
pages/_app.js1import { ClerkProvider, SignedIn, SignedOut } from "@clerk/nextjs";23import { useRouter } from "next/router";45import Head from "next/head";67import Link from "next/link";89// pages that can be accessed without an active user session.1011const publicPages = ["/", "/sign-in/[[...index]]", "/sign-up/[[...index]]"];1213const MyApp = ({ Component, pageProps }) => {14const router = useRouter();1516return (17<ClerkProvider {...pageProps}>18<Head>19<title>Clerk app</title>2021<link rel="icon" href="/favicon.ico" />2223<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />24</Head>2526{/*If the route is for the home, sign-in and sign-up pages: show them without checks.*/}2728{publicPages.includes(router.pathname) ? (29<Component {...pageProps} />30) : (31<>32{/*Show all pages if the user is signed in*/}3334<SignedIn>35<Component {...pageProps} />36</SignedIn>3738{/*Ask to sign in if the user isn't signed in*/}3940<SignedOut>41<main>42<p>43Please{" "}44<Link href="/sign-in">45<a>sign in</a>46</Link>{" "}47to access this page.48</p>49</main>50</SignedOut>51</>52)}53</ClerkProvider>54);55};5657export default MyApp;58
Create the Sign-Up and Sign-In Pages
Next.js uses file-system-based routing, which makes it easy to create new pages. To learn more about Next.js routing check out their official documentation
To create the sign-up and sign-in pages, navigate to the pages/ folder in your project and create two new folders: sign-up/ and sign-in/. Then create a new [[...index]].js file inside both of these folders. These routes will catch all the paths, including /sign-up and /sign-in. You can read more about dynamic routing in the Next.js documentation
Use the prebuilt components for <SignIn/> and <SignUp/> to populate the pages:
pages/sign-up/[[...index]].jsimport { SignUp } from "@clerk/nextjs";const SignUpPage = () => (<SignUp path="/sign-up" routing="path" signInUrl="/sign-in" />);export default SignUpPage;
pages/sign-in/[[...index]].jsimport { SignIn } from "@clerk/nextjs";const SignInPage = () => (<SignIn path="/sign-in" routing="path" signUpUrl="/sign-up" />);export default SignInPage;
Create the Home Page
Now, the home page should display the greeting "Welcome to your new app." at the top of the page. If the user is signed in, it will show them their profile page. Otherwise, it will ask them to sign up or sign in:
Update the `pages/index.js` file to use the `<SignedIn/>` component to conditionally render the child components if the user is signed in and use the `<SignedOut/>` component to render the child components if the user isn't signed in.
Inside the `<SignedIn/>` component, use the `<UserProfile/>` component provided by Clerk to show the user's profile details and allow them to edit their information.
You can also use the `<UserButton />` component in the top `<nav />` to allow users to manage their accounts and sign out of the application. The `<UserButton />` will render as a button with the user's avatar.
Inside the `<SignedOut/>`, render two `<Link />` components to send the user to the sign-in or sign-up page:
pages/index.js1import { SignedOut, SignedIn, UserProfile, UserButton } from "@clerk/nextjs";23import React from "react";45import Link from "next/link";67const Home = () => {8return (9<div10style={{11display: "flex",1213justifyContent: "center",1415alignItems: "center",16}}17>18<main>19<nav20style={{21display: "flex",22justifyContent: "space-between",23alignItems: "center",24}}25>26<h1>Welcome to your new app.</h1>2728<UserButton />29</nav>3031<div>32<SignedIn>33<UserProfile />34</SignedIn>3536<SignedOut>37<Link href="/sign-up">38<a>Sign up </a>39</Link>40or41<Link href="/sign-in">42<a> Sign in </a>43</Link>44to get started.45</SignedOut>46</div>47</main>48</div>49);50};5152export default Home;53
If the user isn't signed in, the page will look like this:
Or if the user is signed in, it will look like this:
When you click the user avatar at the top-right of your screen, a pop-up will appear containing buttons for Manage account and Sign out:
Implementing the User Switcher
Before moving on with this tutorial, you need to navigate to your Clerk dashboard
After enabling multisession handling, go back to your application window and click on the user avatar again. Now you'll see that a new option, Add account, is available:
Clicking on the Add account button will redirect users to the sign-in page, where they can sign in or sign up for a new account.
After signing in, Clerk will redirect the user back to the application with the new session, and the avatar pop-up menu will show all active sessions. The user can now switch between accounts by selecting them from the list:
Authenticating API Endpoints
To prevent malicious requests from coming through, it's essential to authenticate your API endpoints. With Clerk, you can access the user's authentication status in the Next.js API handlers. To do that, you must wrap your API handler function inside Clerk's withAuth higher-order function to access the auth property on the request object.
The following example uses the request.auth property to check if the sessionId is available and then sends the userId in the response. Otherwise, it returns a 401: Unauthorized response code:
pages/api/getUserId.jsimport { withAuth } from "@clerk/nextjs/api";export default withAuth((request, response) => {const { sessionId, userId } = request.auth;if (!sessionId) {return response.status(401).json({ id: null, message: "No user signed in!" });}return response.status(200).json({ id: userId });});
On the home page, add a button to request the API endpoint and show the user ID in an alert:
pages/index.js1import {2SignedOut,3SignedIn,4UserProfile,5SignOutButton,6UserButton,7useAuth,8} from "@clerk/nextjs";910import React from "react";1112import Link from "next/link";1314const Home = () => {15function showUserId() {16fetch("/api/getUserId")17.then((res) => res.json())1819.then(({ id }) => {20alert(`User id: ${id}`);21});22}2324return (25<div26style={{27display: "flex",2829justifyContent: "center",3031alignItems: "center",32}}33>34<main>35<nav36style={{37display: "flex",38justifyContent: "space-between",39alignItems: "center",40}}41>42<h1>Welcome to your new app.</h1>4344<UserButton />45</nav>4647<div>48<SignedIn>49<button onClick={showUserId}>Show user ID</button>5051<UserProfile />5253<SignOutButton />54</SignedIn>5556<SignedOut>57<Link href="/sign-up">58<a>Sign up </a>59</Link>60or61<Link href="/sign-in">62<a> Sign in </a>63</Link>64to get started.65</SignedOut>66</div>67</main>68</div>69);70};7172export default Home;73
After you've added this button, your user switcher is ready:
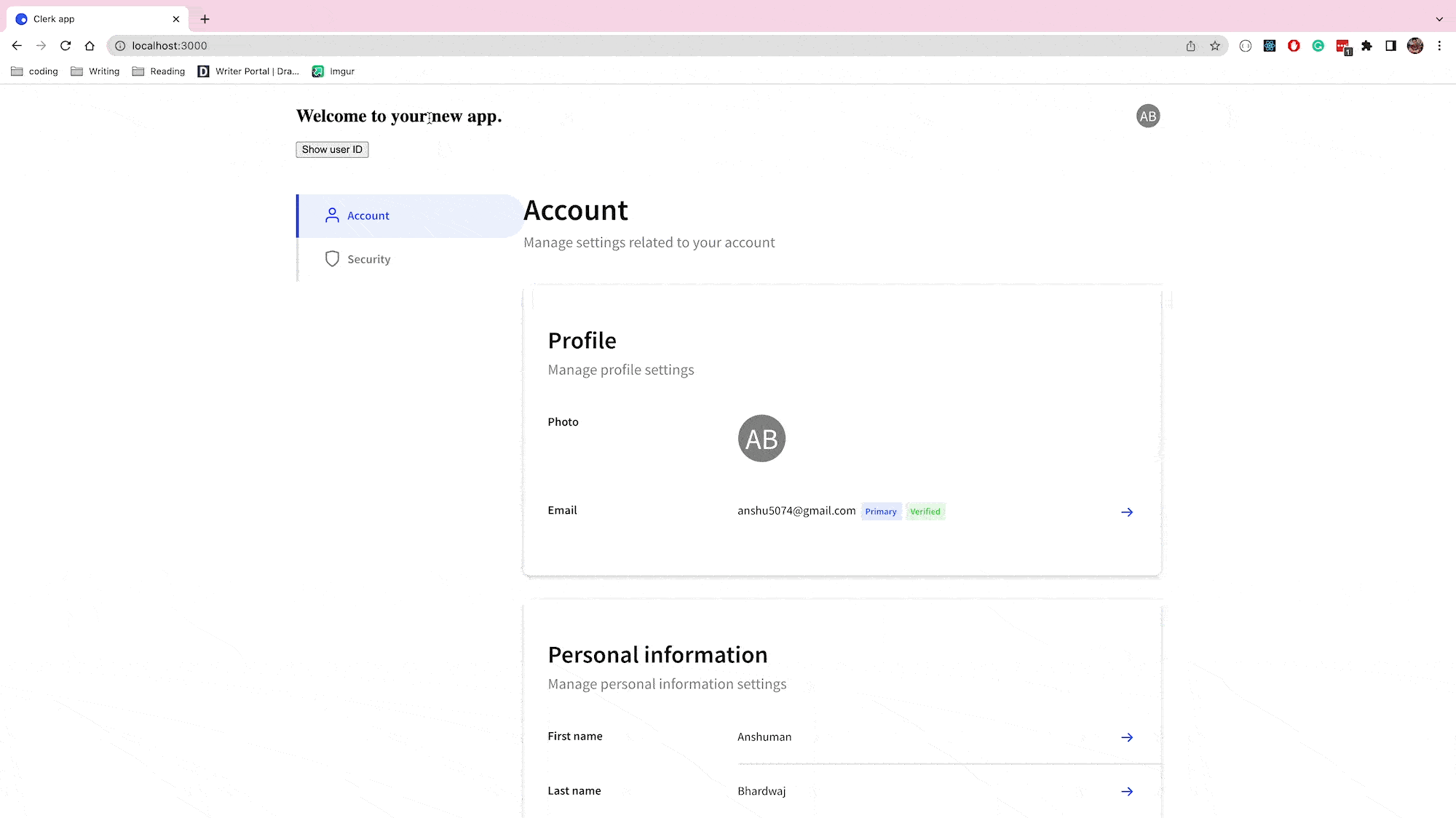
Conclusion
After completing this tutorial, you will have successfully built a Next.js application that supports multisessions. While doing so, you learned about creating a new Next.js application, setting up a Clerk account, and integrating the Clerk SDK with your Next.js application.
You used the UI components provided by Clerk to create an authentication flow and user profile page. You also learned about the importance of multisession support in your application and how easy you can implement it with Clerk. Lastly, you created an API route in Next.js and secured it with Clerk.
Using the Clerk SDK, you can expand on the example above to add social logins and multifactor authentication to your application.
Start now,
no strings attached
Start completely free for up to 5,000 monthly active users and up to 10 monthly active orgs. No credit card required.
Pricing built forbusinesses of all sizes.
Learn more about our transparent per-user costs to estimate how much your company could save by implementing Clerk.
Newsletter!
The latest news and updates from Clerk, sent to your inbox.